Replacing Open-Top Vapor Degreasing in Aerospace Manufacturing
Options and considerations for cleaning aerospace parts as regulations tighten on vapor degreasing solvents.
Open-top vapor degreasers have been used in manufacturing cleaning in the U.S. for over 100 years. The technology has proven throughout that time to be a great cleaning option as it produces clean and dried parts in a one-step process. Utilizing solvent vapors, complex geometry parts can be cleaned effectively and quickly.
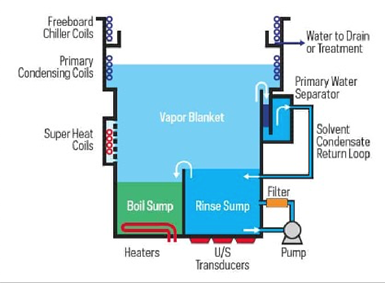
Fig 1: Open-top vapor degreasing
Vapor degreasers use a variety of solvents and have seen an evolution of useable chemistries throughout time, from CFC 113 (commonly referred to by the commercial name Freon and used prior to the Montreal Protocol that phased out chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other substances responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer) to the designer vapor degreasing solvents used today. As the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and regulatory agencies continue to find probable cause to limit or ban specific solvents for environmental or human health reasons, the aerospace industry continuously needs to adapt to the ever-changing guidelines.
Today, the aerospace industry faces major regulations on three commonly used molecules. N-propylbromide (nPB), trichloroethylene (TCE), and perchloroethylene (PERC) are all seeing unprecedented pressure.
The EPA, under the Toxic Substance Control Act (TSCA), is required to evaluate chemicals under a three-stage process. The EPA has determined that nPB, TCE, and PERC pose an unreasonable risk to humans. The proposed limits of these three molecules will prevent any of them from being used in an open-top vapor degreaser.
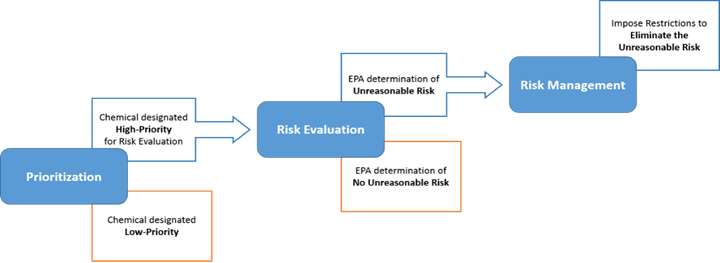
Fig 2: EPA Toxic Substance Control Act (TSAC) evaluation process.
With these solvents becoming unavailable, the industry must look at alternative methods to clean parts. Three viable options are: Drop in solvents, aqueous, and vacuum vapor degreasers.
Drop in Replacement Solvents
There are fluorinated solvents that will be able to be used in an open-top degreaser that will allow the current modern vapor degreaser to be utilized. These fluorinated products are blended with trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene (trans-1,2-DCE, or trans). The trans provides a vast majority of the degreasing power which allows the solvents to be used in vapor only or immersion vapor degreasing processes. The boiling points of these solvents are considerably lower and the degreaser’s heat settings will need to be adjusted. The lower boiling points will prevent the cleaning of some soils with these types of solvents. Also, a consideration is the cost of fluorinated solvents as they are significantly more expensive.
Aqueous
Aqueous cleaning will be a long-term solution for many aerospace manufacturing facilities. There are industry approvals in place that eliminate one concern, the ability to degrease OEM hardware. The chemical blends are seeing some EPA pressure currently. Today, this pressure is somewhat regional around the topics of phosphate and nonylphenol ethoxylate (NPE) surfactants. The NPE surfactants have been banned from use in the European Union (EU) as a part of the REAcH (registration, evaluation and authorization of chemicals) regulations as well as in a few other countries. There are, however, many drawbacks to cleaning with water. Complex part geometry proves to be difficult to clean with many aqueous systems. Aqueous systems require a high floor space cost, higher energy consumption and possible waste stream ramifications. Another significant drawback with aqueous systems is drying the cleaned parts. Drying is often the biggest hurdle in an aqueous process.
Vacuum Vapor Degreasing
Vacuum vapor degreasers are a viable alternative to open-top degreasers for many applications. They employ a closed-loop system that has a very minimal solvent loss. All the benefits of an open-top degreaser are present with the aid of vacuum drying. Vacuum systems, although a great alternative, do come with a significant upfront capital investment. Modified alcohol is one of the solvents used in these systems and lacks many aerospace approvals at this time. Hydrocarbons are another option in this equipment. Again, these lack OEM approvals.

Aerospace fasteners.
Fasteners
An excellent option for cleaning aerospace fasteners is to employ a vacuum vapor degreaser. Because of the small diameters, blind holes, and the need to clean parts numbering into the thousands at a time, a vacuum system is ideal. The struggle to clean these types of parts in an aqueous system is twofold. First, it will be a challenge to ensure all the soils are removed from the surface of each part. Secondly, drying becomes a major challenge.

Water-based cleaning is challenging for parts with complex geometry, making vapor degreasing a good option.
Complex Geometries
A drop-in replacement vapor degreasing solvent is a good option for parts with complex geometries. Water-based cleaning will be a challenge to get the cleaning chemistry to all the blind holes and hard-to-reach areas. As in the previous example, drying becomes a problem with water-based chemistries as well. The vapor from the degreaser will penetrate all areas of the part and will be able to remove the soil. Drying becomes a non-issue with any vapor process. As 3D-printed parts become more and more prevalent in the industry, the need for vapor cleaning will also be in continued demand.
Landing Gear
Large parts such as landing gear that are currently being cleaned in a vapor degreaser can be moved to a water-based cleaning system. The geometries are not overly complex, enabling these parts to be sufficiently cleaned and dried and ready for the next process.
The aerospace industry will no doubt need to adapt soon as commonly used vapor degreasing solvents may become highly regulated. It will be imperative that the correct process type and chemistry is implemented on a part-by-part basis. Lastly, waiting until the last possible moment to begin new process evaluations will be troublesome. Waiting too long will put you at the end of a very long line of new equipment orders already in queue.
Curtis Waters is a process specialist for Brulin Holding Co. Visit brulin.com.
Related Content
Understanding Robotic Vacuum Impregnation
Robotic vacuum impregnation can be used to seal porosity, minimize scrap, increase throughput and reduce costs.
Read MoreVacuum Degreaser Cleans Up a Messy Situation
By replacing its immersion parts washer with a vacuum degreasing system, this machine shop is much more efficient, saving the company money, man hours and the health of the operators.
Read MoreTop Shop Emphasizes Dedication, Work Ethic
With a primary focus on aerospace and defense work, American Metaseal Corp. of Arbutus, Maryland, has qualified as a Top Shop on multiple occasions.
Read MoreMicroCare Offers Alternatives to Discontinued Vapor Degreasing Fluids
MicroCare says it is equipped to handle customers affected by 3M's discontinuation of the Novec specialty fluids line with its own products.
Read MoreRead Next
Education Bringing Cleaning to Machining
Debuting new speakers and cleaning technology content during this half-day workshop co-located with IMTS 2024.
Read MoreEpisode 45: An Interview with Chandler Mancuso, MacDermid Envio Solutions
Chandler Mancuso, technical director with MacDermid Envio discusses updating your wastewater treatment system and implementing materials recycling solutions to increase efficiencies, control costs and reduce environmental impact.
Read MoreA ‘Clean’ Agenda Offers Unique Presentations in Chicago
The 2024 Parts Cleaning Conference, co-located with the International Manufacturing Technology Show, includes presentations by several speakers who are new to the conference and topics that have not been covered in past editions of this event.
Read More





















